
Vitamin B12 Metabolism in Vitamin B2 deficiency
We have got together some of the interdependencies of the vitamins and minerals that are required for maintenance of vitamin B12 function.
Sequentially we have tried to demonstrate what happens under different deficiencies.
Hence the basic methylation pathway, absolute B12 deficiency, functional B12 deficiency due to Molybdenum deficiency, and functional B12 deficiency due to Iodine/and/or Selenium deficiency.
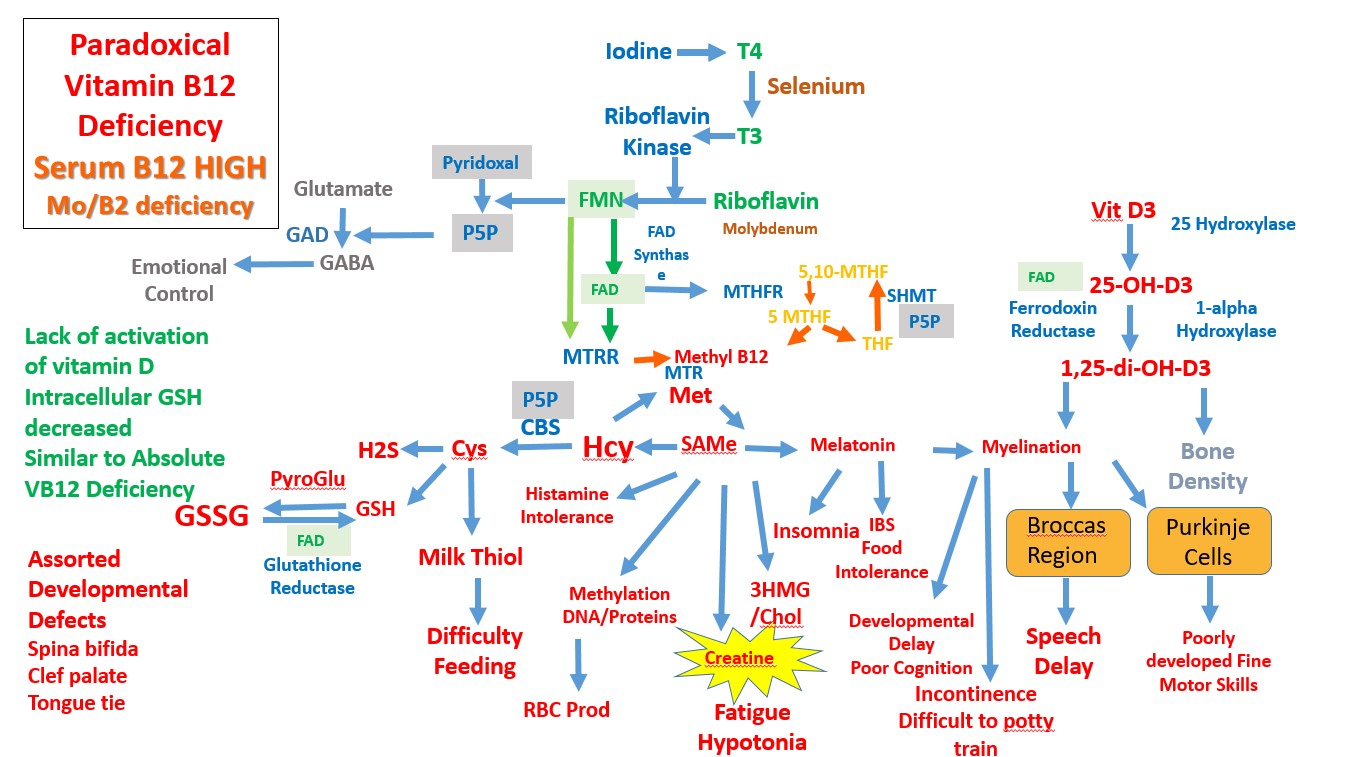
Modification of Methylation pathway in functional B2 deficiency due to Molybdenum deficiency
The effect of functional B2 deficiency due to Molybdenum deficiency, is very similar to that that is seen in absolute vitamin B12 deficiency. However, normally in functional B12 deficiency serum vitamin B12 is normal or high, which is paradoxical (See https://b12oils.com/paradoxical.htm ) .
Lack of production of FAD leads to inactivation of both MTHFR and MTRR, which in turn leads to the build-up of inactive vitamin B12, and as such is very similar to absolute vitamin B12 deficiency. In addition, it will further affect cerebral folate metabolism (Zigman etal, 2021). In addition there are other deficiencies, such as reduced activation of vitamin D.
Intracellular glutathione, that is oxidized to GSSG, is normally reduced by glutathione reductase, an FAD dependent enzyme. Lack of FAD leads to a reduction in the GSH:GSSG ratio, which is common in autism.
Functional B2 deficiency contributes to many of the known metabolic disorders in autism, including the so-called inborn errors of metabolism as described by Zigman and co-workers (2021), including phenylketonuria, homocystinuria, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency, branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase deficiency, urea cycle disorders, organic acidurias (propionic aciduria, L-2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria), cholesterol biosynthesis defects, mitochondrial disorders, lactic acidosis, disorders of purine metabolism lysosomal storage disorders , disorders of copper metabolism (Wilson disease), disorders of haem biosynthesis [acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)] and brain iron accumulation diseases.
OAT analysis shows elevations in lactic acid, glutaric acid, adipic acid, oxalic acid, succinic acid, suberic acid, sebacic acid, and hippuric acid, all indicative of functional B2 deficiency, and supporting the concept of so-called inborn errors of metabolism.
Molybdenum deficiency also results in an intolerance to sulphites, and may contribute to some symptoms of food sensitivity
References
Richdale etal, 2023 Pathways to anxiety and depression in autistic adolescents and adults. Depression and Anxiety Volume 2023 | Article ID 5575932 |
vitamin-b12-deficiency-and-depression-what-is-the-mechanism.pdf (aseanjournalofpsychiatry.org)
Russell-Jones GJ 2022 Functional B2 deficiency in autism REF
Russell-Jones GJ 2022 Functional vitamin B12 deficiency in autism REF2
Žigman T, Petković Ramadža D, Šimić G, Barić I. Inborn Errors of Metabolism Associated With Autism Spectrum Disorders: Approaches to Intervention. Front Neurosci. 2021 May 28;15:673600. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.673600. PMID: 34121999; PMCID: PMC8193223.
Copyright © 2014 B12 Oils. All Rights Reserved.
Reproduction in whole or in part in any form or medium without express written
permission is prohibited