Vitamin B12 Metabolism
We have got together some of the interdependencies of the vitamins and minerals that are required for maintenance of vitamin B12 function.
Sequentially we have tried to demonstrate what happens under different deficiencies.
Hence the basic methylation pathway, absolute B12 deficiency, functional B12 deficiency due to Molybdenum deficiency, and functional B12 deficiency due to Iodine/and/or Selenium deficiency.
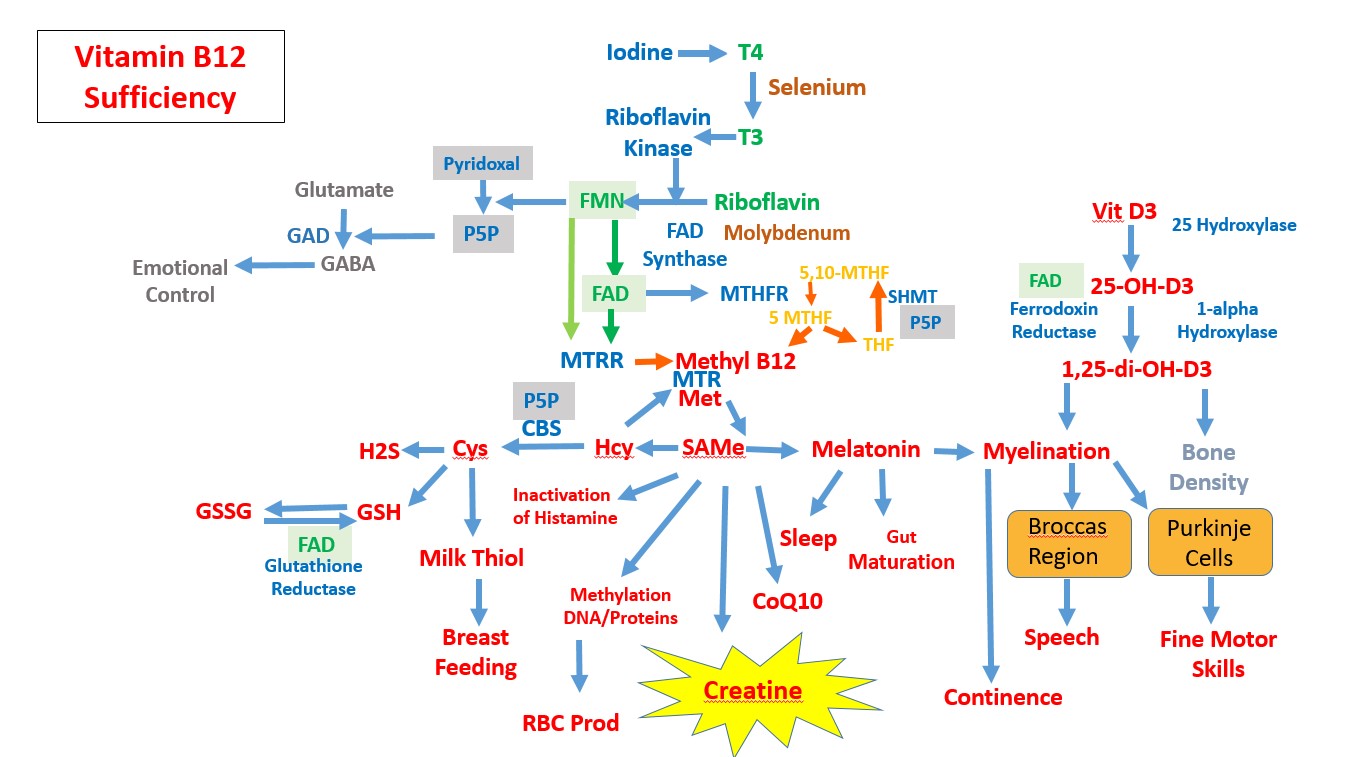
Methylation in Methyl B12 sufficiency
Methylation is also required for the formation of Melatonin, in which the enzyme Hydroxyindole-O-Methyltransferase using SAMe to methylate NAcetylSerotonin to form Melatonin. Melatonin then functions in the maturation of the gut wall, in the process of sleep, and in the stimulation of differentiation of neuronal step cells to form myelin-producing oligodendrocytes. Myelination precedes the development of speech, development of fine motor skills, development of the frontal cortex, and in myelination of the phrenic nerve for the development of continence. In the process of myelination melatonin works in combination with vitamin D to stimulate neuronal stem cells to differentiate into myelin-producing oligodendrocytes. Myelination of nerves leads to a dramatic increase in the nerve conduction speed, increasing it from 2.5 metres per second to over 150 metres per second. Myelination thus has an essential role in increasing the processing speed in the brain, thus increasing academic performance, cognition, intellectual development, reasoning, and experience.
Methylation is required for the formation of S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe), which is used by over 200 methylation enzymes.
SAMe is used by the enzyme Guanidinoacetate-N-Methyl-transferase, which is the enzyme that is involved in the formation of creatine, the major energy transport molecule inside the cytoplasm of the cell. The major sites of creatine synthesis are the muscles and the brain. Creatine is also required for enhanced cognitive function, and neuropsychological performance.
Methylation is required for the conversion of phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylchoine, the precursor for the production of choline. Choline is reacted with acety-CoA to form the neurotransmitter acetyl-choline. Acetylcholine is used in arousal, attention, memory and motivation.
There are 3 methylation steps involved in the formation of CoQ10, the major energy shuttle vector within the Electron Transport Chain.
Functional vitamin B2, Selenium and the B12 activation pathway
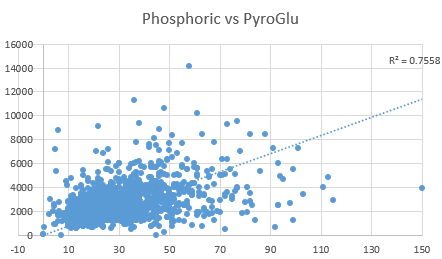
From the metabolic pathway presented above, it can be seen that activation of vitamin B12 is critically dependent upon functional vitamin B2, which in turn is dependent upon Iodine, Selenium and Molybdenum. Whilst this pathway seems simple there is a co-founding inter-dependency of each of B2, Se and B12. Hence, functional vitamin B12 is required to raise levels of S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM), but SAM in turn is required for activation of the B6-dependent enzyme CBS, which is involved in converting homocysteine to cystathionine. Cystathionine, is then required for the formation of cysteine, and the sub-sequent formation of glutathione (GSH), which is maintained in its reduced state by the FAD-dependent enzyme glutathione reductase. In a metabolic twist GSH is required for the formation of GSSeSG complex with Selenite, which is then reduced to release the HSe- intermediate for the formation of Selenophosphate, and then the SeCys-tRNA. Hence Selenium is required for the conversion of T4 to T3, with subsequent production of FMN and FAD, BUT, FAD is required for both B12 cycling, to then create Cys, then GSH, and also for maintenance of Glutathione reductase to process the selenite. This can lead to the reaction being "Stuck" when Selenium levels are low, T3, low, then functional B12 low, and then there is an inability to process incoming selenite. The RDA for Selenite is 55-200 ug/day, which is around 2 orders of magnitude than Methionine, but the RDA for Methionine - which has to be repeatedly recycle is 3 gm. Hence to get significant conversion of SeMet => SeHomocysteine => SeCyst, one would have to completely saturate the pathway with SeMet, which would then also result in the incorrect insertion of Se-Met into the bodies proteins, with resultant undesirable sequelae. When Selenite is extremely low, it can be very hard to start up the pathway. OAT analysis shows generation of large quantities of Pyroglutamate, and increased urinary phosphoric acid, indicating lack of activity of the iron-sulphur protein Adrenodoxin (Russell-Jones 2024).
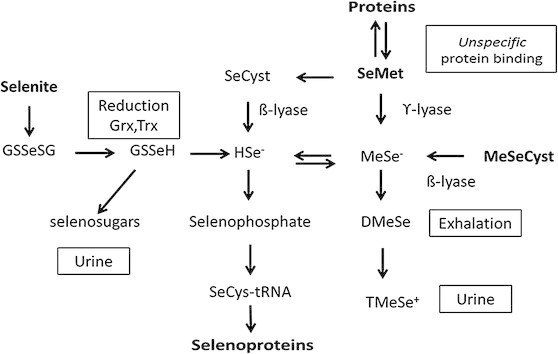
Interdependency of functional B2 on Selenite processing.