
Research Findings - Bulgaria
We have been retrospectively examining data obtained from parents of children who have autism/developmental delay, to see if there is any basic differences in the Biochemistry between countries. We have separated out the Hair Metals Test Analysis (HMTA) data and Organic Acids Test (OAT) data, and present the findings in graphical form below.
HMTA
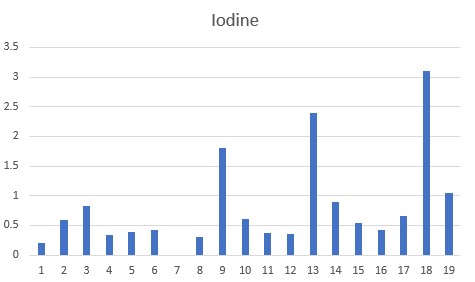
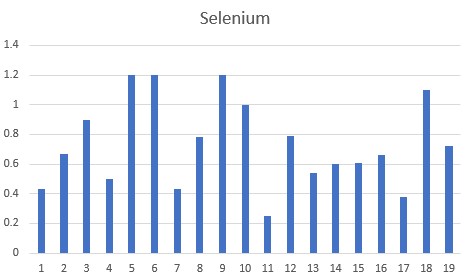
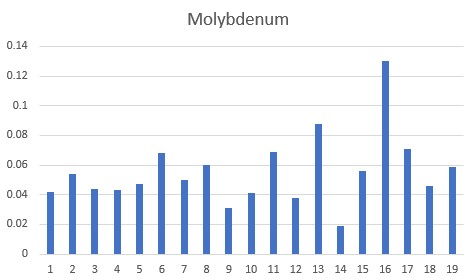
Previous data has shown that in Modern Day Autism, the major precipitating factor is functional B2 deficiency due to deficiencies in Iodine, Selenium and/or Molybdenum, all of which are required to activate vitamin B12. We present this data below. As can be seen all of the children were deficient in one or more of Iodine (<1.0 ppm : 15/18), Selenium (<1.0 ppm 14/19), or Molybdenum (<0.08 ppm: 13/19), with dual deficiencies being common. Hence, the data would suggest that these children would have functional vitamin B2 deficiency. The observation of Iodine deficiency in the children is consistent with data on the known Iodine deficiency in Bulgaria (Stoeva etal, 1997; Delange, 2002; Møllehave etal, 2022). The observed Selenium deficiency has also been reported for much of Europe, including Bulgaria (Alehagen etal, 2015).
OAT
Previous data has shown that in Modern Day Autism, the major precipitating factor is functional B2 deficiency due to deficiencies in Iodine, Selenium and/or Molybdenum, all of which are required to activate vitamin B12. This in turn can be seen in alterred metabolism in OAT.
We present this data below.
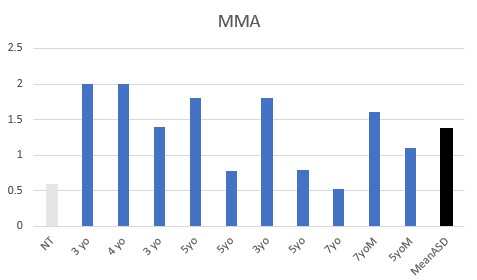
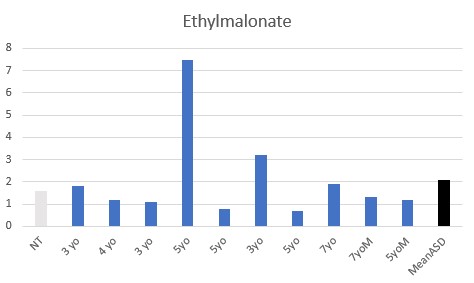
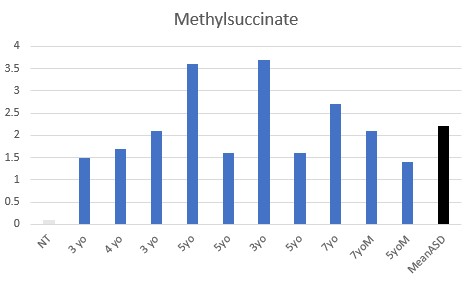
All children had functional deficiency in Adenosyl vitamin B12, with elevated MMA being common and elevated methylsuccinate universal.
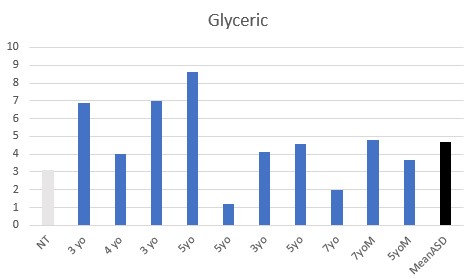
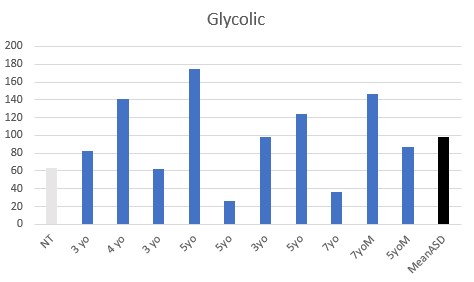
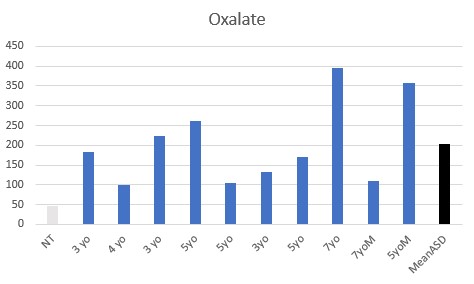
Functional vitamin B2 deficiency was seen in all the children, with various levels of elevated oxalate, lactate, and succinate.
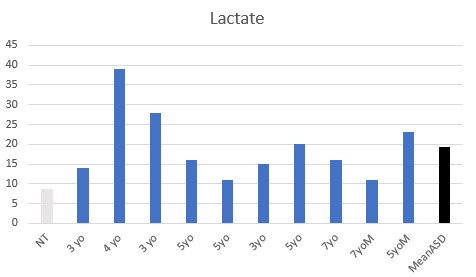
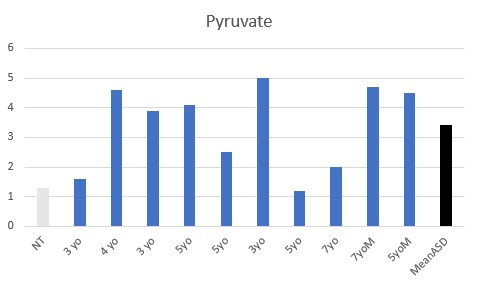
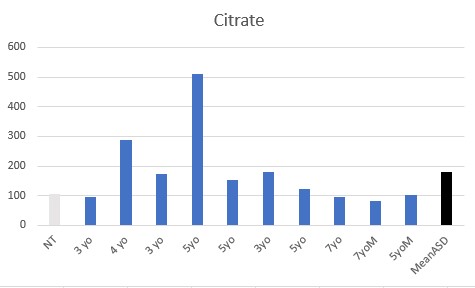
In contrast to data from other countries, children in Bulgaria, generally were iron sufficient, suggesting that the observed functional B12 deficiencies seen were as a result of the functional B2 deficiencies observed.
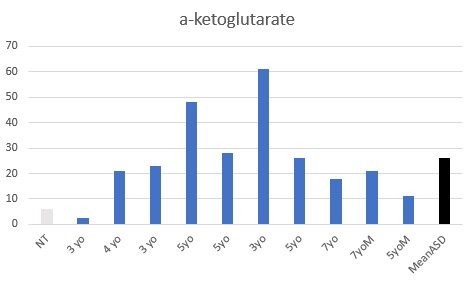
Vitamin B1 deficiency was common (9 of 10), as judged by elevated AKG, and elevated pyruvic acid. This is commensurate with a gluten-free diet, which was common in the children.

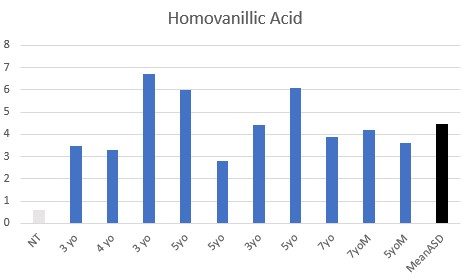
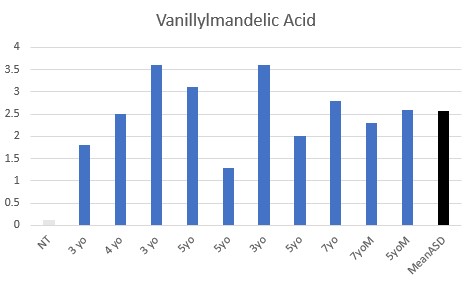
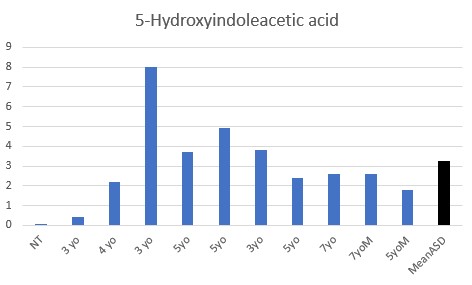
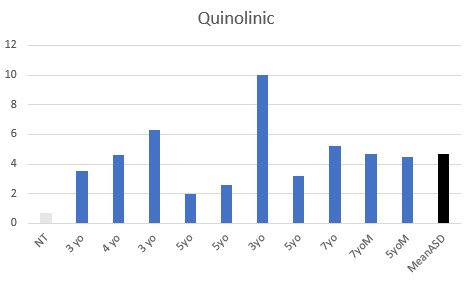
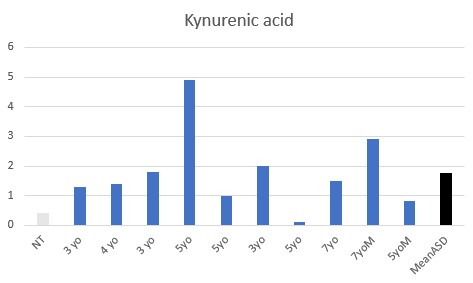
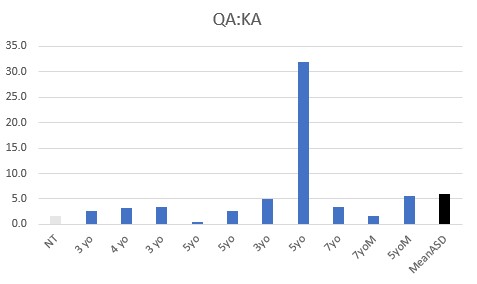
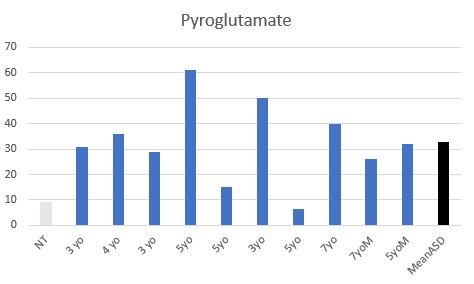
All children were functionally deficient in Methyl B12 as judged by VMA, HVA, 5HIAA, QA, and KA, with elevated pyroglutamic acid being common.
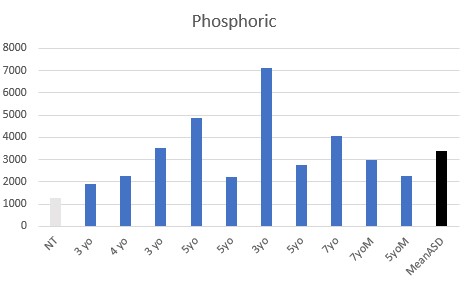
All children showed some degree of vitamin D deficiency as judged by elevated phosphoric acid.
Publications
Stoeva I, Peneva L, Grigorova R, Vassileva B, Brumm H, Grüters A. Neonatal TSH screening--an instrument of iodine supplementation monitoring in Bulgaria in comparison to Berlin--a preliminary report. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1997;105 Suppl 4:51-4. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211933. PMID: 9439916.
Delange F. Iodine deficiency in Europe and its consequences: an update. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002 Aug;29 Suppl 2:S404-16. doi: 10.1007/s00259-002-0812-7. Epub 2002 Jun 1. PMID: 12192540.
Møllehave LT, Eliasen MH, Strēle I, Linneberg A, Moreno-Reyes R, Ivanova LB, Kusić Z, Erlund I, Ittermann T, Nagy EV, Gunnarsdottir I, Arbelle JE, Troen AM, Pīrāgs V, Dahl L, Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A, Trofimiuk-Müldner M, de Castro JJ, Marcelino M, Gaberček S, Zaltel K, Puig-Domingo M, Vila L, Manousou S, Nyström HF, Zimmermann MB, Mullan KR, Woodside JV, Völzke H, Thuesen BH. Register-based information on thyroid diseases in Europe: lessons and results from the EUthyroid collaboration. Endocr Connect. 2022 Mar 10;11(3):e210525. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0525. PMID: 35044931; PMCID: PMC8942317.
Alehagen U, Aaseth J. Selenium and coenzyme Q10 interrelationship in cardiovascular diseases--A clinician's point of view. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2015;31:157-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.11.006. Epub 2014 Nov 27. PMID: 25511910.
Copyright © 2018 B12 Oils. All Rights Reserved.
Reproduction in whole or in part in any form or medium without express written
permission is prohibited